Best Wire for Sale What to Know Before You Buy?
In the world of construction and DIY projects, finding the right wire for sale is crucial. Tim Johnson, a noted expert in electrical wiring, once said, "Choosing the right wire can make or break your project." His words highlight the importance of selecting quality materials.
When buying wire, various factors come into play. Consider the type of wire you need: copper or aluminum? Each has its benefits and drawbacks. Pricing can also vary widely. Shoppers must beware of potential scams. An alluring price may hide inferior quality.
It's easy to overlook essential details in this crowded marketplace. Do not rush your decision. Take time to research different suppliers. Reviews and recommendations are invaluable resources. Skipping this step could lead to costly mistakes. Ensure you're buying from reputable vendors. Ultimately, the right wire can enhance safety and efficiency in your projects.

Factors to Consider When Choosing Electrical Wire for Your Project
When selecting electrical wire, several factors come into play. Wire gauge is critical. Thicker wires can carry more current but are also more expensive. According to the National Electrical Code, using the correct gauge can prevent overheating and ensure safety. A 12-gauge wire is typical for general-purpose circuits in homes.
Insulation type is another crucial consideration. Different insulation materials, like PVC or THHN, offer varying degrees of heat resistance and flexibility. A report by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers highlights that improper insulation can lead to deterioration and safety hazards over time. This decision can impact the life span of your installation significantly.
Lastly, environmental conditions matter. If the wire will be exposed to moisture, UV rays, or chemicals, choosing the right type is essential. Experts suggest that failing to account for these factors leads to premature wire failure. Overlooking specifications may save money initially but can lead to costly repairs later. You must weigh quality against budget constraints carefully.
Different Types of Electrical Wires and Their Applications Explained
When selecting electrical wires, understanding their types is crucial. Various wires serve specific functions. For instance, THHN wires are great for indoor use. They resist heat and moisture well. If you're wiring a home, this may be your go-to option.
Another popular choice is Romex. It's a type of non-metallic sheathed cable. Perfect for residential work, it simplifies installation. However, it's not suitable for outdoor applications. Pay attention to your project requirements before making a choice.
Here are some tips to consider: Always check the wire gauge. It impacts the amount of current a wire can safely carry. Also, consider the environment. Some wires are better suited for wet conditions. Lastly, don't overlook the insulation type. It plays a critical role in safety and performance.
Best Wire for Sale What to Know Before You Buy?
| Wire Type | Material | Gauge | Application | Max Voltage (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper Wire | Copper | 12 | Residential Wiring | 600 |
| Aluminum Wire | Aluminum | 10 | Heavy-duty Application | 600 |
| Solar Wire | Copper | 14 | Solar Panel Connections | 600 |
| PVC Insulated Wire | Copper | 16 | General Electronics | 300 |
| Speaker Wire | Copper | 18 | Audio Systems | 120 |
Understanding Wire Gauge: How It Affects Current Flow and Safety
When choosing wire, understanding wire gauge is crucial. Wire gauge determines the thickness of the wire. Thicker wires can carry more current safely. For instance, a wire with a 10 AWG gauge can handle up to 30 amps, while a 16 AWG wire only handles about 10 amps. This difference significantly affects electrical safety.
Consider this: using a wire that's too thin for high current can lead to overheating. Overheated wires can cause fires or equipment damage. A report from the National Fire Protection Association indicates that electrical failures caused by inadequate wiring are a significant risk in residential fires. Remember, not all projects require heavy-duty wire. Evaluate your needs carefully.
Here are some tips:
1. Always check the ampacity ratings for your specific wire gauge.
2. Don’t overlook the insulation type; it impacts safety and durability.
Choosing the right wire is not always straightforward. Sometimes, personal judgment may lead to errors. Balance expedience with thorough checks.
The Importance of Voltage Rating in Selecting the Right Wire
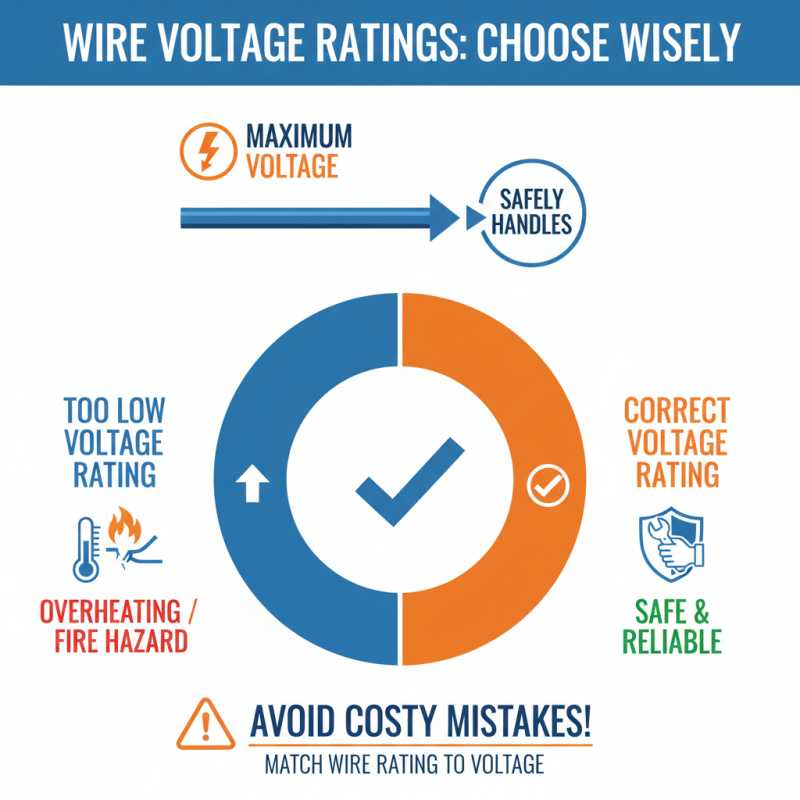
When selecting the right wire, understanding voltage ratings is crucial. Voltage ratings indicate the maximum voltage a wire can safely handle. Using a wire with an insufficient rating can lead to overheating or even fires. Choose wisely to avoid costly mistakes.
Tips: Always check the wire's specifications before buying. Look for clear labels on the packaging to ensure safety.
Higher voltage means greater potential, and wires must be suited for that purpose. Factors like insulation type also affect the wire's capability. Some insulation can withstand higher temperatures, leading to more durability. Don't overlook these details, as they matter significantly in wiring decisions.
Tips: Consider future needs when choosing wire. You may require more power later on. Opt for a wire that can grow with your demands.
Comparing Copper vs. Aluminum Wires: Pros, Cons, and Cost Analysis

When deciding between copper and aluminum wires, it’s crucial to consider their characteristics. Copper wires are more conductive. This means they allow electricity to flow more freely. According to industry reports, copper has a conductivity of about 59.6 million S/m. In contrast, aluminum’s conductivity is around 37.7 million S/m. This difference impacts energy efficiency and performance.
Aluminum wires offer lower initial costs. They are often cheaper to produce, making them attractive for large projects. However, aluminum is less durable than copper. Over time, aluminum wires can corrode. This may lead to higher maintenance costs.
Tips: Always consider the long-term implications of your choice. Sometimes, the cheaper upfront cost can lead to higher expenses down the line. If you choose aluminum, ensure it is properly treated to reduce corrosion risks. Keep in mind that poor installation can negate its benefits.
Furthermore, safety is vital. Copper wires are less likely to overheat. This can make a significant difference in high-load situations. Aluminum can expand and contract more than copper which may lead to loose connections over time. A loose connection can cause overheating and potential hazards. Think about these factors carefully.
Related Posts
-

Top Tips for Finding the Best Wire for Sale Online?
-

How to Choose the Right Welding Cable for Your Project?
-
2026 Best 3 Core Cable Selection for Your Electrical Projects?
-

10 Best Multi Conductor Cables for Superior Electrical Performance in 2023
-
How to Select the Right MC Cable for Your Electrical Projects
-
2026 Top Multi Conductor Cable Types and Their Applications?
