How to Choose the Right 3 Core Cable for Your Electrical Projects
When embarking on electrical projects, selecting the appropriate cable type is crucial to ensure safety, efficiency, and compliance with regulatory standards. Among the various options available, the 3 core cable stands out as a versatile choice, particularly for applications requiring additional functionality, such as the incorporation of earth connections. According to industry reports, the global demand for multi-core cables is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7.4% from 2021 to 2028, highlighting the increasing reliance on robust wiring solutions in both residential and commercial sectors.
Choosing the right 3 core cable not only contributes to the functionality and longevity of electrical systems but also plays a significant role in accident prevention. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) emphasizes that improperly selected cables can lead to overheating and potential fire hazards. Data from the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) indicates that electrical failures are one of the leading causes of structure fires, accounting for approximately 13% of the total reported fires in the U.S. Therefore, informed decision-making regarding cable specifications—including conductor size, material, and insulation type—remains imperative for anyone undertaking electrical installations or upgrades.
In summary, understanding the importance of selecting the correct 3 core cable is fundamental to any electrical project. With increasing regulatory requirements and safety standards, it is essential for professionals and DIY enthusiasts alike to stay abreast of the latest specifications and best practices to ensure their projects are completed not only effectively but also safely.
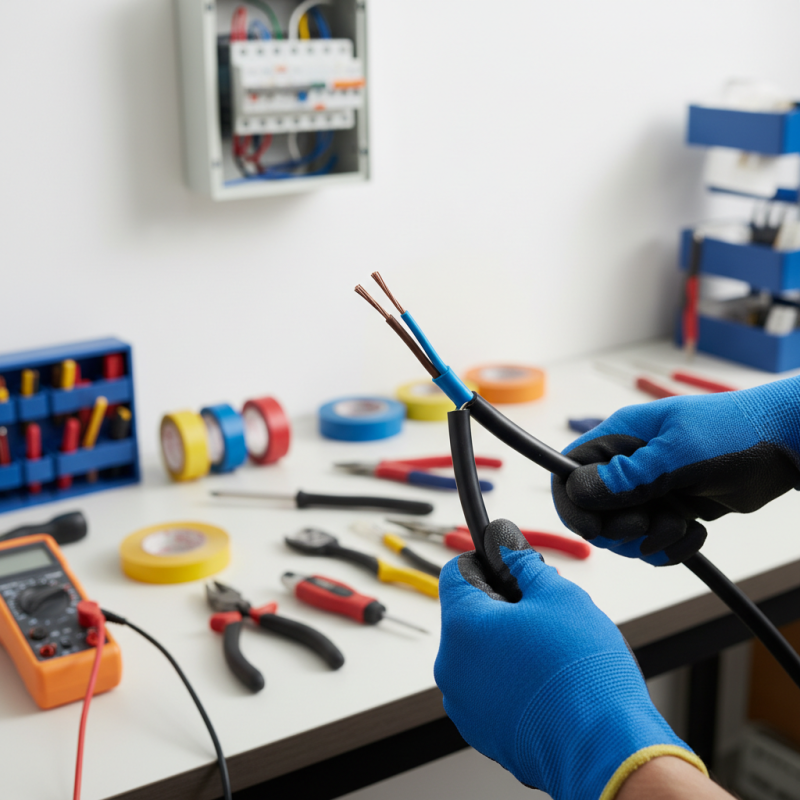

Understanding the Basics of 3 Core Cables in Electrical Projects
When embarking on electrical projects, understanding the basics of 3 core cables is essential for ensuring safety and efficiency. A 3 core cable typically consists of three conductors: live, neutral, and earth. The live wire carries current to the load, the neutral wire carries current away, and the earth wire provides a safe path for fault current. According to the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), utilizing properly rated conductors can significantly reduce the risk of electrical hazards, which is crucial for both residential and industrial applications.
The choice of insulation material and cable size is equally important. For example, PVC and XLPE are the most commonly used insulation materials, each offering distinct temperature ratings and mechanical protection suitable for various environments. Industry reports indicate that the demand for high-quality cables, such as those designed to endure extreme conditions, is increasing at a rate of 6% annually. Additionally, understanding the National Electrical Code (NEC) guidelines can further enhance safety, as compliance reduces the risk of short circuits and fire hazards. Hence, grasping these foundational aspects of 3 core cables not only helps in making informed choices but also ensures the longevity and reliability of electrical installations.
Understanding the Applications of 3 Core Cables
Identifying the Key Specifications for 3 Core Cables
When selecting the appropriate 3 core cable for your electrical projects, understanding the key specifications is crucial for ensuring safety and efficiency. The first critical specification to consider is the cable's conductor material, typically made of either copper or aluminum. Copper is known for its excellent conductivity and durability, making it a common choice for many applications. On the other hand, aluminum is lighter and less expensive but may require larger diameters to carry the same current. Assessing the conductor material based on the specific demands of your project will significantly influence performance.
Another important factor is the cable's cross-sectional area, which is measured in square millimeters (mm²). This dimension directly relates to the amount of current the cable can safely carry without overheating. For residential circuits, common sizes range from 1.5 mm² for lighting circuits to 2.5 mm² for power circuits. Additionally, it’s vital to consider the voltage rating and insulation type of the cable. Different insulation materials provide varying degrees of resistance to heat, moisture, and chemicals, making them suitable for different environments. By carefully evaluating these specifications, you can select a 3 core cable that meets both the regulatory standards and the functional requirements of your electrical project.
Evaluating Material Types for Optimal Performance and Durability

When selecting the right 3 core cable for your electrical projects, understanding the various material types is crucial for achieving optimal performance and durability. The three primary materials used for cable conductors are copper, aluminum, and steel. Copper is renowned for its excellent conductivity, flexibility, and resistance to corrosion, making it an ideal choice for applications where efficiency is paramount. Aluminum, while not as conductive as copper, is lighter and more cost-effective, making it suitable for larger installations where weight and budget are considerations. Steel is often utilized for its strength and durability but is less common in standard electrical applications due to its inferior conductive properties.
In addition to the conductor materials, the insulation and sheath also play a vital role in the cable's performance. Common insulation materials include PVC, XLPE, and rubber, each offering different degrees of thermal resistance and environmental protection. PVC is widely used for its affordability and adequate performance in most indoor applications, while XLPE provides superior thermal and moisture resistance, making it ideal for more demanding environments. Rubber sheaths, though often more expensive, offer excellent flexibility and resilience against mechanical damage. By carefully evaluating the material types and their properties, you can ensure that the chosen 3 core cable will not only meet the requirements of the project but also withstand the test of time in the intended application.
Assessing Cable Size and Current Rating for Your Needs

When undertaking electrical projects, selecting the appropriate 3 core cable is crucial for ensuring safety and efficiency. One of the primary considerations in this selection is assessing the cable size and its current rating, which can vary significantly based on the application. According to the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), it is vital to refer to the National Electrical Code (NEC) guidelines, where the recommended current ratings for various cable sizes can be found. For instance, a 1.5mm² cable typically supports a maximum current of 18-20 Amperes, depending on environmental factors. Understanding these specifications helps to prevent overheating and ensures the longevity of the electrical system.
Moreover, ambient temperature and installation conditions also affect the current-carrying capacity of cables. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) states that every 10°C increase in temperature can reduce the current rating significantly, necessitating recalculations to ensure compliance with safety standards. When assessing your electrical needs, it's essential to consider factors such as load demand and the number of circuits in use. For example, in residential applications where multiple devices may run simultaneously, opting for a larger diameter cable can provide a buffer that accommodates peak load demands without compromising performance. By diligently evaluating these aspects, you can ensure your electrical projects are both safe and efficient.
Choosing the Right Insulation and Protection for 3 Core Cables
When selecting 3 core cables for your electrical projects, the choice of insulation and protection is paramount. Insulation materials determine how effectively the cable can withstand environmental factors such as moisture, temperature variations, and external mechanical damage. Common insulation types include PVC, XLPE, and rubber, each offering different advantages based on the application. For instance, PVC is widely used for its excellent electrical properties and cost-effectiveness, while XLPE provides superior thermal resistance and is suitable for higher temperatures. Understanding the specific needs of your project will guide you in choosing the most suitable insulation material.
In addition to insulation, the protective layer of a 3 core cable should not be overlooked. The protective sheath safeguards the cable from physical damage, chemical exposure, and abrasion. Choosing the right material for the protective layer—such as steel wire armoring for heavy-duty applications or a simple PVC sheath for lighter uses—depends largely on the environment in which the cable will be installed. Factors like potential exposure to rodents, UV rays, and harsh weather conditions must be considered to ensure longevity and reliability. Ultimately, a well-chosen insulation and protective strategy will enhance the performance and lifespan of your electrical installations.
How to Choose the Right 3 Core Cable for Your Electrical Projects
| Cable Type | Conductor Material | Insulation Type | Voltage Rating (V) | Current Rating (A) | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H05VV-F | Copper | PVC | 300/500 | 10 | Indoor Wiring |
| H07RN-F | Copper | Rubber | 450/750 | 16 | Outdoor Equipment |
| NYM-J | Copper | PVC | 300/500 | 20 | Fixed Installations |
| SY Cable | Copper | PVC | 300/500 | 32 | Flexible Applications |
Related Posts
-

Top Types of Cable Wire You Need to Know for Effective Wiring Solutions
-

Top Electrical Connectors for Reliable Performance in Your Projects
-

Top 10 Benefits of Using 2 Wire Systems for Efficient Connectivity
-
Understanding the Benefits and Uses of Romex Wire in Modern Electrical Installations
-

Understanding Lead Cables: Essential Insights for Safe Electrical Installations
-
Top 10 Control Cable Types for Optimal Performance in Industrial Applications
