How to Choose the Right Welding Cable for Your Projects in 2025
As the welding industry continues to evolve, selecting the appropriate welding cable becomes increasingly critical for ensuring efficiency and safety in various projects. In 2025, welders must consider a range of factors when choosing welding cables, including the type of welding processes they utilize, the environment in which they work, and the specific electrical requirements of their tasks. An informed choice can greatly impact the overall performance of welding equipment and the quality of the finished product.
Welding cables come in various sizes, materials, and insulation types, each designed for specific applications and environments. Understanding these differences is essential for welders who aim to achieve optimal results while maintaining safety standards. Aspects such as voltage rating, flexibility, and resistance to heat or abrasion play vital roles in the performance and longevity of welding cables.
In this guide, we will explore the key criteria for selecting the right welding cable for your projects in 2025, empowering you to make informed decisions that enhance your welding capabilities. Whether you are a professional welder or a hobbyist, the right welding cable is a crucial component that should never be overlooked.

Understanding the Types of Welding Cables Available in 2025
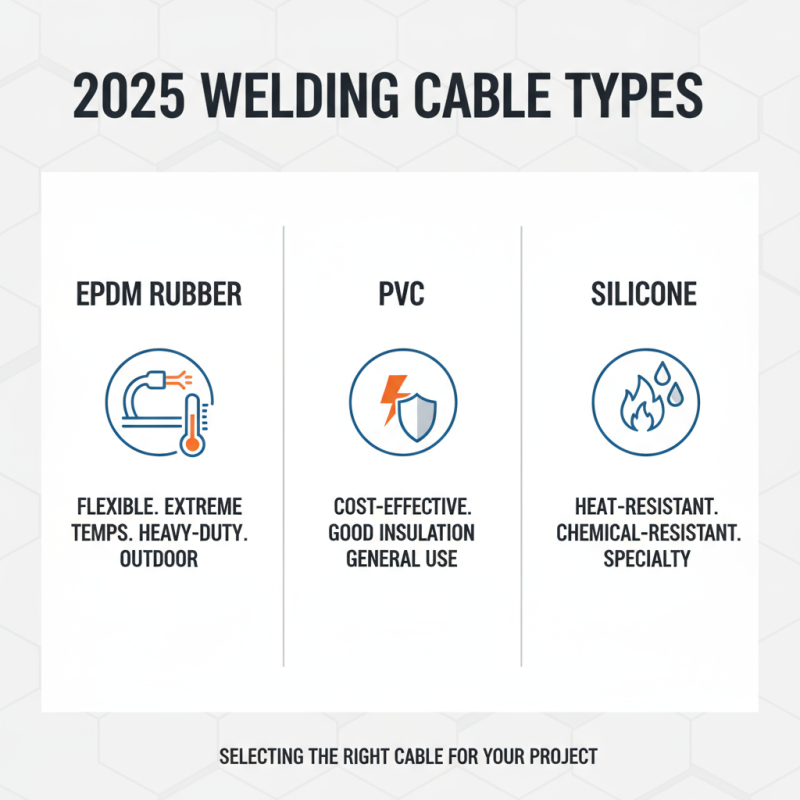
In 2025, selecting the appropriate welding cable for your projects involves understanding the various types available in the market. Welding cables are categorized primarily based on their construction, size, and insulation materials. The most common types include EPDM rubber, PVC, and silicone-insulated cables. Each material offers unique benefits; for instance, EPDM rubber cables excel in flexibility and resistance to extreme temperatures, making them ideal for outdoor and heavy-duty applications.
Moreover, cable size is crucial in ensuring efficiency and safety during welding processes. The American Wire Gauge (AWG) system is typically used to determine the appropriate wire thickness, which should be matched to the amperage requirements of the welding machine. For high amperage applications, a thicker cable with a lower AWG rating is recommended to minimize resistance and heat generation. Additionally, understanding the length of the cable is essential, as longer cables may require a larger diameter to maintain energy levels and performance. By grasping these key factors, welders can make informed decisions tailored to their specific project needs.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting Welding Cable for Your Project
When selecting welding cable for your projects in 2025, several key factors come into play that can significantly influence the performance and safety of your work. First and foremost, it is essential to understand the appropriate gauge of the cable. The gauge determines the ampacity, which refers to the maximum current the cable can handle without overheating. A thicker cable (lower gauge number) is necessary for high-amperage applications, while lighter tasks can utilize thinner cables. Always consider the specific requirements of your welding techniques and equipment to ensure optimal performance.
Another critical aspect to consider is the insulation type of the welding cable. Given the harsh environments that welding often entails, choosing a cable with robust insulation is vital for durability. Materials like rubber and thermoplastic elastomer provide excellent flexibility and resistance to abrasions and heat, which can enhance the longevity of the cable. Additionally, it is crucial to ensure that the cable can withstand the specific environmental challenges, such as exposure to oils, chemicals, or extreme temperatures. By prioritizing these factors, you can select a welding cable that not only meets project specifications but also ensures safety and efficiency in your welding operations.
Welding Cable Selection Factors in 2025
Assessing the Ampacity Ratings for Welding Cables
When selecting the appropriate welding cable for your projects in 2025, understanding ampacity ratings should be one of your primary considerations. Ampacity refers to the maximum amount of electric current a conductor or device can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. It is essential to choose a welding cable that matches or exceeds the ampacity required for your specific application. This ensures safety and efficiency, preventing overheating and potential failures during welding operations.
Evaluating the ampacity ratings involves considering factors such as the cable’s size, insulation material, length, and ambient temperature. Larger diameters generally have higher ampacity, making them more suitable for heavy-duty tasks. Additionally, cables with superior insulation materials can withstand higher temperatures, which is crucial in welding environments where heat is constantly a concern. It is also advisable to account for the installation conditions and whether the cables will be used in open air or enclosed spaces, as these factors can significantly influence the effective ampacity of the cable. By taking these considerations into account, you can ensure optimal performance and longevity of your welding cables.
Evaluating Cable Insulation and Jacket Materials for Durability
When selecting the right welding cable for your projects in 2025, evaluating cable insulation and jacket materials is crucial for ensuring durability and safety. The insulation material protects the conductive core from environmental factors and hazards, while the jacket serves as an additional layer of protection against abrasion, chemicals, and heat. According to the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), the most commonly used insulation materials in welding cables are thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). TPE offers superior flexibility and resistance to heat and chemicals, making it an excellent choice for demanding work environments.
Furthermore, the jacket material plays a significant role in the longevity of the welding cable. Reports from the American Welding Society (AWS) indicate that cables with rubber or urethane jackets demonstrate better performance in rugged conditions compared to those with lesser-quality materials. This is particularly important for outdoor welding tasks where exposure to UV rays, extreme temperatures, and moisture can degrade cable integrity. In studies, cables with high-quality insulation and jackets have shown a 30% increase in lifespan compared to those made with lower-grade materials, underscoring the importance of making informed choices based on the specific demands of your projects.
How to Choose the Right Welding Cable for Your Projects in 2025 - Evaluating Cable Insulation and Jacket Materials for Durability
| Cable Type | Insulation Material | Jacket Material | Temperature Rating (°C) | Max Voltage (V) | Durability Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type A | PVC | Rubber | 90 | 600 | High |
| Type B | EPDM | Thermoplastic | 105 | 800 | Very High |
| Type C | Silicone | Neoprene | 150 | 1000 | Extreme |
| Type D | PVC | Synthetic | 80 | 500 | Medium |
Matching Welding Cable Length and Flexibility to Your Application

When selecting the right welding cable for your projects in 2025, it is crucial to match the length and flexibility of the cable to the specific requirements of your application. A report from the Welding Institute highlights that the optimal cable length can significantly enhance efficiency and reduce the risk of electrical resistance, which can lead to overheating and poor weld quality. For instance, using a cable length that exceeds the necessary requirements can lead to increased power loss, estimated at approximately 3% for every 100 feet of additional length beyond what is needed. Hence, measuring the distance from your power source to the welding site will help you determine the most efficient cable length.
Flexibility is another vital factor that can impact the effectiveness of welding operations. According to a study by the National Association of Manufacturers, cables with higher flexibility ratings allow for easier maneuverability and reduced fatigue during prolonged use, which is particularly important for projects that require frequent repositioning of equipment. Cables designed with flexible materials can handle tight bends and varying workspaces, enabling welders to maintain a consistent performance level. Prioritizing flexibility not only promotes worker comfort but also enhances product efficiency, ensuring that welding tasks are completed with precision and minimal downtime.
Related Posts
-

2025 Top 10 Marine Cable Innovations Transforming Global Connectivity
-
Exploring the Advantages of 4 Core Cable in Modern Electrical Installations and Its Impact on Efficiency
-
Top 10 Benefits of Using Soow Cable for Your Electrical Wiring Needs
-

2025 Top 10 Multi Conductor Cables for Industrial Applications You Must Know
-
Understanding the Essential Role of Wire and Cable in Modern Technology Systems
-

Understanding the Importance of Electric Cable Wire in Modern Technology
