Top 3 Core Cable Types You Need to Know for Your Electrical Projects
In the realm of electrical projects, understanding the types of cables utilized is paramount for ensuring safety and efficiency. Among the various options available, the "3 core cable" stands out for its versatility and reliability. According to a recent industry report by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), the adoption of multi-core cables, including 3 core configurations, has increased by 25% over the past five years, reflecting their growing importance in modern electrical installations.
Expert in electrical engineering, Dr. Emily Johnson, highlights the significance of 3 core cables within the industry, stating, "The reliability and safety provided by 3 core cables cannot be overstated; they are essential in preventing electrical faults and ensuring compliance with stringent safety standards." This emphasizes the need for project managers and electricians to have a thorough understanding of 3 core cable types and their appropriate applications.
As we delve into the top three core cable types that are vital for your electrical projects, it is crucial to recognize how selecting the right cable not only enhances operational effectiveness but also contributes to the overall safety of electrical installations. By being informed about 3 core cables, one can make better decisions that align with current best practices in electrical engineering.
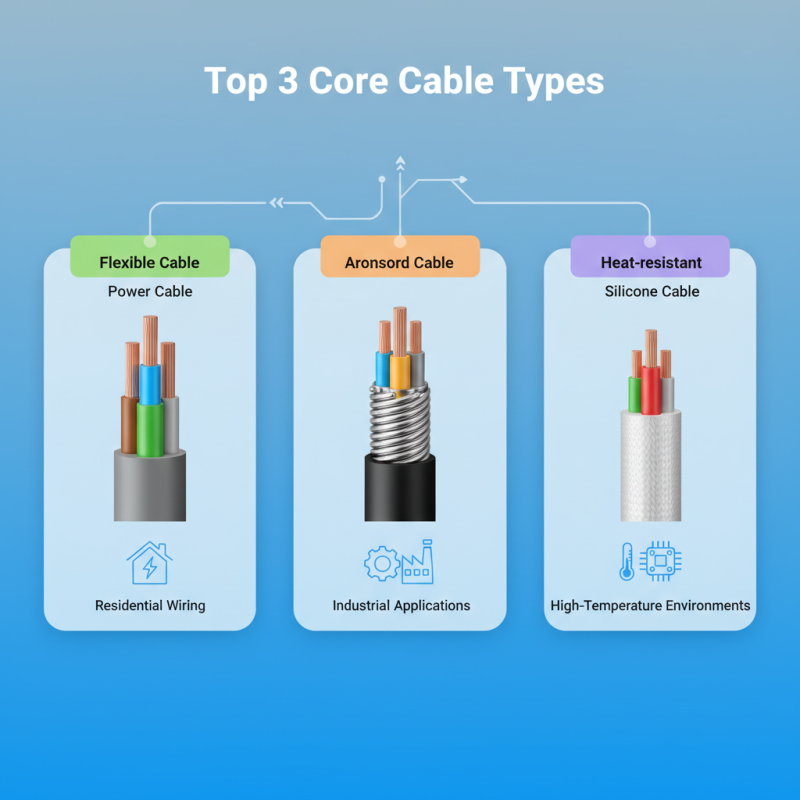
Understanding the Importance of Core Cable Types in Electrical Projects
Understanding the various core cable types is essential for anyone involved in electrical projects, whether it's for residential, commercial, or industrial applications. Core cables serve as the backbone of electrical systems, providing the necessary pathways for electricity to travel safely and efficiently. Each type of core cable is designed for specific applications and environments, which makes knowing their characteristics crucial. For instance, some cables are insulated for protection against moisture and chemical exposure, while others are designed for high-temperature environments.
Selecting the appropriate core cable type not only ensures compliance with safety standards but also enhances the overall reliability of your electrical system. Using the wrong cable can lead to increased resistance, power loss, or even system failures. Each cable type has distinct attributes that dictate its capacity to withstand certain environmental conditions, current loads, and voltage levels. Understanding these elements allows you to make informed decisions that can improve both the performance and longevity of your electrical projects. By investing time in learning about core cable types, you can significantly reduce risks and enhance efficiency in your electrical installations.
Top 3 Core Cable Types for Electrical Projects
The chart above illustrates the efficiency ratings of the top three core cable types commonly used in electrical projects. Copper cables are known for their excellent conductivity, while aluminum cables offer a lightweight alternative with decent efficiency. Fiber optic cables, while different in function, showcase strong performance in data transmission efficiency.
Overview of Cable Types: Standards and Specifications in Electrical Work
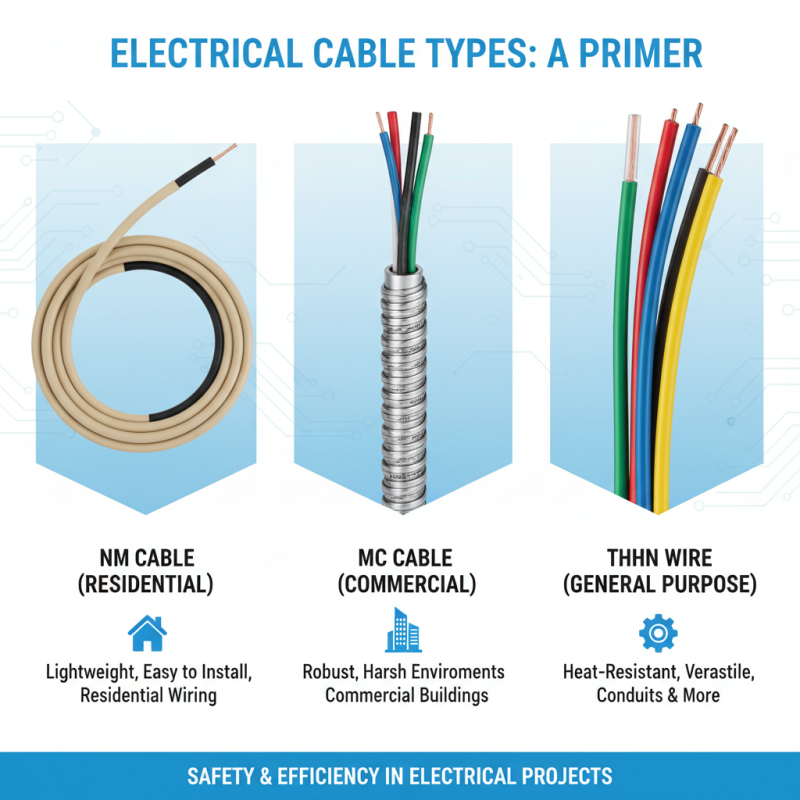
When embarking on electrical projects, understanding the various types of cables is crucial for ensuring safety and efficiency. The key cable types commonly used include NM (non-metallic) cable, MC (metal-clad) cable, and THHN (Thermoplastic High Heat-resistant Nylon-coated) wire. Each of these cable types adheres to specific standards that dictate their construction, insulation, and application areas. For instance, NM cable is often favored for residential wiring because it is lightweight and easy to install, while MC cable is utilized in commercial settings due to its robustness and ability to withstand harsher environments.
In addition to the cable types, it's essential to consider the relevant specifications that govern their usage. Electrical codes, such as the National Electrical Code (NEC) in the United States, lay out guidelines for installation practices and material choices to promote safety. Understanding factors such as voltage ratings, temperature ratings, and environmental considerations will inform the selection of the appropriate cable for a project. Adhering to these standards helps to prevent electrical failures and hazards, ensuring that the installed systems operate efficiently and securely.
Copper Vs. Aluminum Cables: Strengths, Weaknesses, and Applications
When it comes to electrical projects, understanding the differences between copper and aluminum cables is crucial.
Copper cables have long been the industry standard due to their superior conductivity, which is approximately 60% better than that of aluminum. This means that copper cables can carry the same amount of current with a smaller gauge, leading to reductions in installation space and overall weight. Moreover, copper exhibits excellent resistance to corrosion, making it a reliable choice for long-term applications, especially in harsh environments.
On the other hand, aluminum cables present a more cost-effective solution while still offering adequate performance for specific applications. According to the National Electrical Contractors Association (NECA), aluminum cables are about 40% lighter than their copper counterparts, making them easier to install, particularly in overhead lines and large installations. However, aluminum wires tend to have greater thermal expansion properties, requiring careful installation practices to prevent potential issues like loose connections over time.
Tips: When choosing between copper and aluminum cables, consider the long-term operational costs. For high-load installations, copper may offer better reliability and efficiency, while for standard applications with less strain, aluminum can provide significant savings. Always ensure proper installation techniques to maximize safety and performance, regardless of the cable type selected.
Applications of THHN and THWN Cables in Residential and Commercial Projects
THHN and THWN cables are two of the most common types of wires used in both residential and commercial electrical projects. THHN stands for Thermoplastic High Heat-resistant Nylon-coated wire, which is designed to withstand high temperatures and is suitable for dry locations. This makes THHN an excellent choice for wiring inside residential homes, connecting appliances, and powering lighting systems. Its versatility also extends to commercial environments where equipment requires robust and heat-resistant wiring solutions.
On the other hand, THWN stands for Thermoplastic Water-resistant Nylon-coated wire, which is similar to THHN but is designed to be water-resistant. This characteristic makes THWN ideal for outdoor applications or in any setting where the cable might be exposed to moisture. It is commonly used in underground installations and wet locations, providing the necessary protection against water damage. Both cable types meet stringent safety and performance standards, making them crucial components in any electrical project, whether at home or within commercial buildings. Understanding the specific applications and benefits of THHN and THWN cables can significantly enhance the efficiency and safety of electrical systems.
The Role of Armored and Non-Armored Cables in Safety and Performance
When it comes to electrical projects, the choice between armored and non-armored cables is crucial for ensuring both safety and performance. Armored cables are designed to provide enhanced protection against mechanical damage, making them ideal for environments exposed to harsh conditions. The metallic sheath serves as a barrier against physical impacts, thereby safeguarding the inner conductors from potential hazards. This makes armored cables particularly suitable for outdoor installations, construction sites, and industrial applications where durability is a priority.
On the other hand, non-armored cables are more flexible and easier to install in scenarios where extreme protection is not necessary. These cables are often sufficient for residential wiring and indoor applications where they are less likely to encounter damaging forces. However, choosing non-armored options requires careful assessment of the installation environment to avoid potential risks. Ultimately, understanding the specific roles and applications of armored and non-armored cables is vital for making informed decisions that ensure reliable performance and safety in any electrical project.
Top 3 Core Cable Types You Need to Know for Your Electrical Projects
| Cable Type | Armored/Non-Armored | Primary Use | Safety Features | Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NM Cable | Non-Armored | Residential wiring | Low voltage rating, lightweight | Good for interior applications |
| AC Cable | Armored | Commercial applications | Durable, moisture resistant | Excellent mechanical protection |
| UF Cable | Non-Armored | Underground installations | Direct burial, moisture resistant | High resistance to environmental conditions |
Conclusion
Understanding the various types of core cables is essential for successful electrical projects. This article emphasizes the significance of selecting the right core cable type based on standards and specifications critical to both residential and commercial applications. A comparison between copper and aluminum cables highlights their respective strengths and weaknesses, aiding in the decision-making process for specific projects.
Furthermore, it delves into the applications of THHN and THWN cables, alongside the roles of armored and non-armored cables in ensuring safety and performance. Finally, the article discusses the importance of calculating electrical load requirements to choose the appropriate cable size, thus ensuring the efficiency and reliability of electrical systems. By focusing on these aspects, professionals can gain a comprehensive understanding of the vital 3 core cable types necessary for any electrical undertaking.
Related Posts
-

How to Choose the Right 3 Core Cable for Your Electrical Projects
-

Essential Automotive Cable Maintenance Tips for a Smooth Ride
-
Top 5 Core Cable Types That You Need To Know For Your Projects
-

Maximizing Safety and Efficiency: The Essential Guide to Choosing Electrical Wire Connectors in 2023
-
What is Armoured Cable? Understanding Its Types, Benefits, and Applications
-

2025 Top 5 Industrial Electric Wire and Cable Solutions for Every Business Need
