Top 4 Core Cable Types for Reliable Electrical Connections?
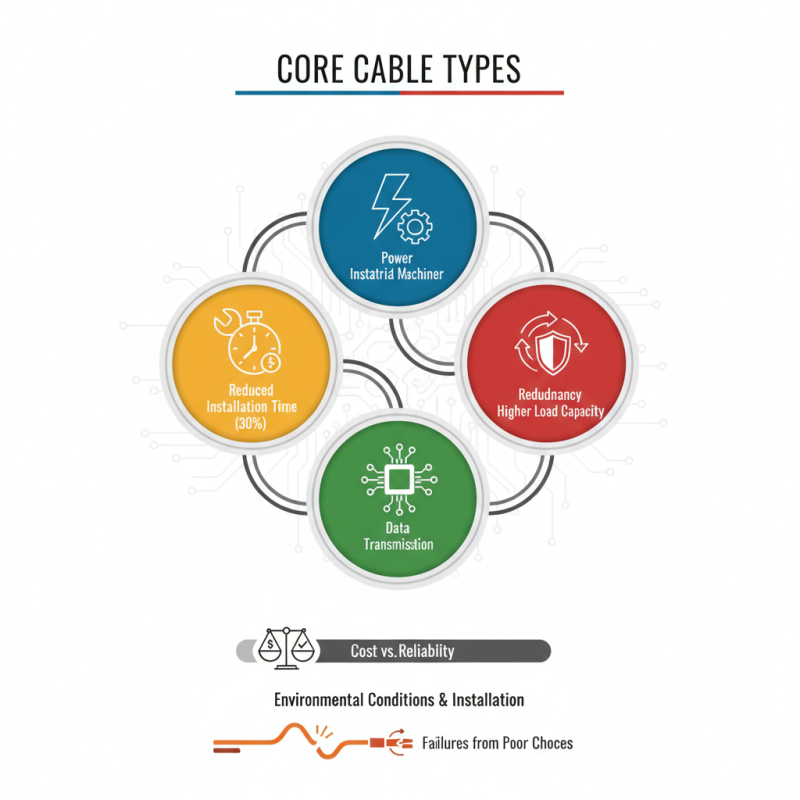
In the electrical industry, reliability is paramount. The choice of cables significantly impacts performance. Among various types, 4 core cable stands out. This cable type has four conductors, ensuring effective power distribution and signal integrity. Reports show that using multi-core cables can reduce installation time by up to 30%.
The versatility of 4 core cable makes it ideal for diverse applications. It is commonly used in power installations, industrial machinery, and data transmission. According to data from industry experts, multi-core configurations provide better redundancy. They can also support higher load capacities. However, selecting the right type of cable can be a challenge.
Even with the advantages, there are parameters to consider. Factors like environmental conditions and installation practices can influence performance. Some projects may overlook the importance of quality materials. As a result, poor choices lead to failures. It's crucial to balance cost with reliability for long-term success.
Top 4 Core Cable Types for Reliable Electrical Connections
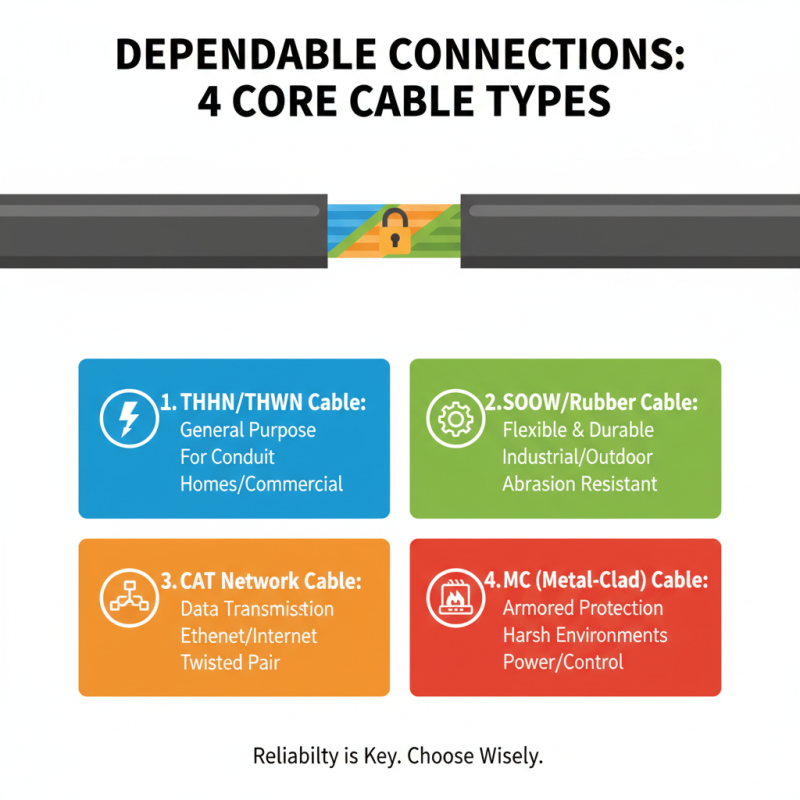
When choosing core cables, reliability is key. Different cable types serve various electrical needs. Here are four core cable types to consider for dependable connections.
Copper cables are popular for their excellent conductivity. Their flexibility makes them suitable for various installations. However, they can be prone to corrosion in damp environments. Regular inspections can help mitigate this issue.
Aluminum cables are lighter and more cost-effective. They are often used in overhead power lines. Yet, they may require larger diameters to carry the same current as copper. Pay attention to connections, as they can expand and contract with temperature changes.
Tips: Always match the cable type to the specific electrical load. This ensures safety and efficiency. Additionally, consider the installation environment. Harsh conditions can impact cable performance.
Lastly, consider using multi-stranded cables for higher flexibility. They are easier to handle in tight spaces. However, they may not carry current as efficiently as solid wires. The installation process must be well-planned to avoid issues later. Each type has advantages and challenges that need careful thought.
Understanding the Importance of Electrical Cable Types in Connectivity
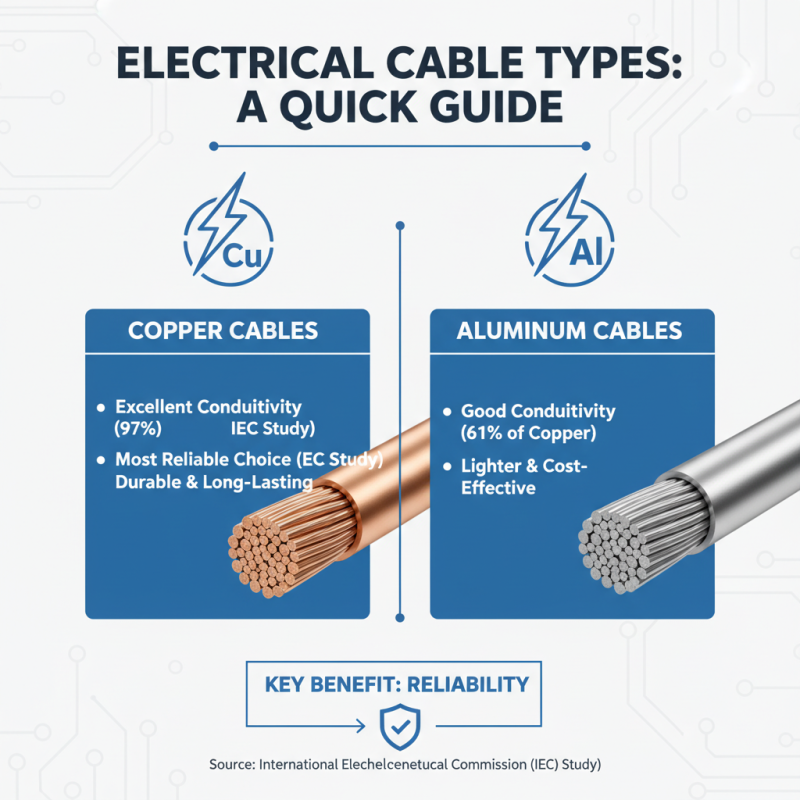
When it comes to electrical connections, understanding the type of cable used is crucial. Different cable types offer various benefits that impact connectivity and performance. For instance, copper cables are known for excellent conductivity. According to a study by the International Electrotechnical Commission, copper remains the most reliable choice for electrical applications, showing a conductivity level of 97% compared to aluminum.
In contrast, aluminum cables are lighter and more cost-effective. However, their conductivity is about 61% of copper's. This difference can lead to potential energy loss over long distances. Data from the National Electrical Manufacturers Association highlights that improper cabling can result in energy inefficiencies, leading to increases in operational costs. Many installations overlook the significance of cable type, often prioritizing budget over long-term reliability.
Fiber optic cables, on the other hand, offer high-speed data transfer with minimal signal loss. They are essential in modern telecommunications. However, the installation process can be complex and costly. A report from the Optical Fiber Communication Conference indicates that the adoption of fiber optics is growing, yet many organizations still rely on outdated cabling solutions. This reliance can hinder overall network performance.
Comparative Analysis of Copper vs. Aluminum Cables in Performance
When comparing copper and aluminum cables, several factors impact their performance. Copper cables tend to have higher conductivity. According to the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), copper has a conductivity of 59.6 MS/m. In contrast, aluminum’s conductivity is about 37.7 MS/m. This significant difference means that copper can transmit electricity more efficiently than aluminum.
However, aluminum cables have their advantages. They are lighter and usually less expensive, making them a popular choice for certain applications. A report from the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) shows that aluminum can weigh up to 60% less than copper for the same amount of current. This weight reduction simplifies installation. Yet, this same lightness can lead to potential issues in long-term reliability, as aluminum can expand and contract more than copper.
Durability also plays a crucial role in the discussion. Copper resists corrosion better than aluminum. Over time, aluminum can oxidize, affecting the connection quality. According to a study by the American Society of Civil Engineers, corrosion issues account for up to 30% of electrical failures in improperly installed aluminum systems. Evaluating these factors helps in making informed choices for reliable electrical connections.
Performance Comparison of Copper and Aluminum Cables
Key Features of XLPE Cables for Enhanced Electrical Insulation
XLPE cables, or cross-linked polyethylene cables, have gained attention for their exceptional performance in electrical insulation. Industry reports highlight that these cables can withstand a temperature range of -40°C to 90°C. Such endurance is crucial for various applications, particularly in challenging environments. This property makes XLPE ideal for power distribution networks and renewable energy systems.
One remarkable feature of XLPE cables is their superior dielectric strength. According to a recent report from the International Electrotechnical Commission, XLPE cables can endure electric fields exceeding 20 kV/mm. This high resistance reduces the risk of electrical failures. Moreover, the low moisture absorption of XLPE enhances its longevity. Over time, this may minimize replacement costs and operational disruptions for companies.
However, some challenges remain. The manufacturing process can produce inconsistencies in cable quality. Rainwater ingress or poor installation techniques may compromise the cable's performance. Regular inspections and adherence to installation guidelines are vital. Emphasizing quality control in the production line is essential for consistent results in XLPE cable performance. Addressing these issues proactively can enhance the reliability of electrical connections.
Applications and Efficiency of PVC Cables in Electrical Systems
PVC cables are popular in various electrical systems due to their efficiency and versatility. They are widely used for residential wiring, industrial applications, and public infrastructure. These cables are lightweight, making installation easier. The flexibility of PVC insulation allows for easier maneuvering in tight spaces.
In addition to their practicality, PVC cables come with high resistance to moisture and chemicals. This makes them suitable for diverse environments. However, one must consider temperature limits. At high temperatures, PVC can become less efficient. It may even degrade over time. Proper installation and regular monitoring can help mitigate these issues.
One area for improvement is biodegradability. PVC cables are not environmentally friendly and can contribute to waste. Recycling options exist, but they are limited. As we move towards more sustainable practices, the demand for alternative materials grows. This ongoing challenge emphasizes the need for innovation in cable technology and material science.
Top 4 Core Cable Types for Reliable Electrical Connections
| Cable Type | Material | Voltage Rating | Applications | Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVC Cable | Polyvinyl Chloride | 600V | Residential Wiring | High |
| XLPE Cable | Cross-linked Polyethylene | 1kV - 35kV | Industrial Applications | Very High |
| Rubber Cable | Rubber Insulation | 450V - 750V | Construction & Outdoor | Moderate |
| Armored Cable | Steel & PVC | 600V | Mining & Heavy Industry | High |
Related Posts
-

2026 Top Electrical Wire Connectors for Every Project Need?
-

Understanding Multi Conductor Cables: Essential Tips for Effective Electrical Wiring
-
2026 Best 3 Core Cable Selection for Your Electrical Projects?
-
What is Armoured Cable? Understanding Its Types, Benefits, and Applications
-
Understanding the Essential Role of Wire and Cable in Modern Technology Systems
-

Top 10 Uses of Thermocouple Wire in Industrial Applications
