Top 5 Core Cable Types That You Need To Know For Your Projects
When embarking on electrical projects, understanding the various types of cables available is crucial for ensuring safety and efficiency. Among them, the "5 core cable" stands out as a versatile option suitable for a wide array of applications. This type of cable is designed to accommodate five different conductors, providing the ability to power multiple circuits or devices simultaneously. Whether you are working on residential installations, industrial setups, or commercial projects, having a solid grasp of core cable types can significantly enhance the quality and reliability of your work.
In this article, we will explore the top five core cable types that are essential for your projects. Each type comes with unique characteristics and benefits, making them ideal for specific applications. From understanding their construction and functionality to considering factors such as flexibility, insulation, and installation requirements, this guide aims to equip you with the knowledge you need to make informed decisions. By the end, you will have a clearer perspective on the role of 5 core cables and other essential cable types, ensuring that your projects are executed smoothly and effectively.
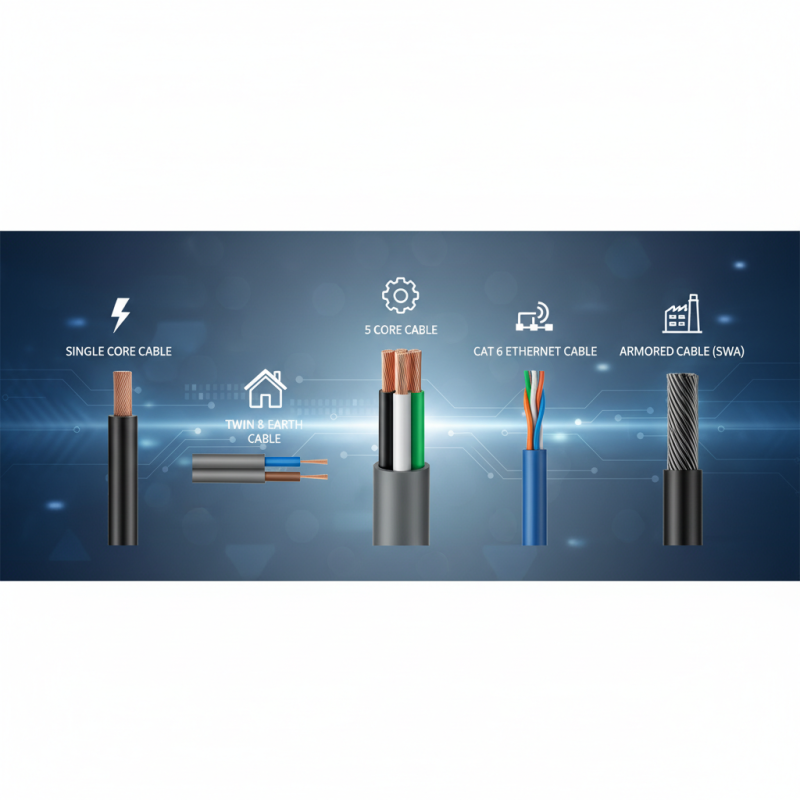

Understanding the Importance of Core Cables in Project Development
Core cables play a pivotal role in various projects, making them an essential aspect of project development. Understanding the significance of core cables is crucial for ensuring the success and efficiency of any electrical or communication project. These cables serve as the backbone for transmitting power and data across systems, facilitating seamless connectivity. Their ability to support high-speed data transfer and maintain power integrity is vital in today’s fast-paced technological environment, where delays or failures can result in significant setbacks.
Moreover, the correct selection of core cable types according to project specifications can greatly influence overall performance and longevity. Factors such as load capacity, environmental conditions, and compatibility with existing systems must be carefully considered. By prioritizing the right core cables, project developers can enhance safety, improve efficiency, and reduce maintenance costs in the long run. In conclusion, recognizing the importance of core cables equips project managers with the knowledge to make informed decisions, ultimately leading to successful project outcomes.
Overview of Different Core Cable Types and Their Applications
Core cables are essential components in various electrical and telecommunications projects, providing critical connectivity and power delivery. Understanding the different types is vital for selecting the appropriate cable for specific applications. The main core cable types include twisted pair, coaxial, fiber optic, and power cables, each with unique characteristics and uses.
Twisted pair cables, commonly found in data communication and telephony, consist of pairs of insulated wires twisted together, which aids in reducing electromagnetic interference. According to a report by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), twisted pair cables account for approximately 70% of total networking cables used globally, primarily in local area networks (LANs) and telephone systems. Their affordability and ease of installation make them a go-to choice for many projects.
Coaxial cables, featuring a central conductor surrounded by insulation and an outer conductive shield, are mainly utilized for broadband internet and cable television services. A market analysis by Mordor Intelligence indicated that the global coaxial cable market is expected to grow by 5.4% annually, driven by the increasing demand for high-speed internet services. Finally, fiber optic cables are quickly gaining traction due to their high bandwidth capacity and speed, making them suitable for modern data centers and telecommunications networks. The Fiber Optic Association reports that fiber optic technology can transmit data over long distances at speeds exceeding 1 Gbps, highlighting their pivotal role in the future of connectivity.
Top 5 Core Cable Types and Their Applications
Detailed Examination of Copper Core Cables: Benefits and Use Cases
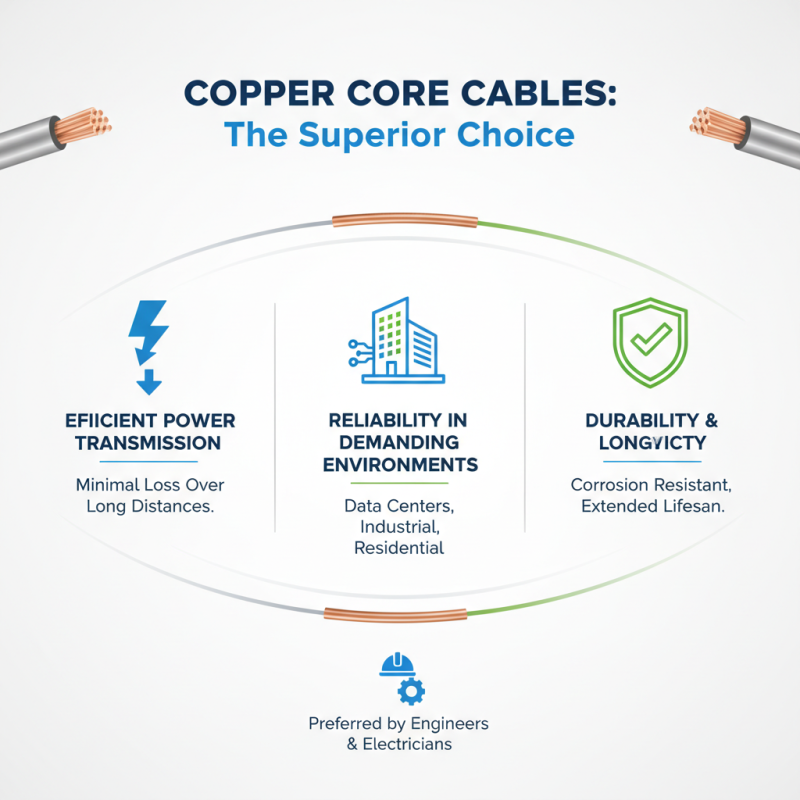
Copper core cables are a fundamental component in many electrical and telecommunications applications, owing to their excellent conductivity and reliability. One of the primary benefits of copper core cables is their ability to efficiently transmit electricity over long distances with minimal loss. This characteristic makes them ideal for high-demand environments such as data centers, industrial applications, and residential installations. Their durability and resistance to corrosion also enhance their lifespan, further making them a preferred choice among project engineers and electricians.
In addition to their electrical performance, copper core cables offer significant versatility in various use cases. They can be found in everything from power distribution networks to residential wiring, ensuring safe and efficient electricity delivery. Furthermore, copper’s pliability allows for easy handling and installation, particularly in complex environments where maneuverability is crucial. The thermal conductivity of copper also contributes to its effectiveness, as it helps to dissipate heat generated during operation, reducing the risk of overheating and failure in critical systems. These attributes underscore why understanding copper core cables is essential for anyone involved in planning or executing electrical projects.
Exploring Fiber Optic Cables: Advantages for Modern Telecommunication
Fiber optic cables have revolutionized the landscape of modern telecommunication, providing significant advantages over traditional copper cables. One of the most compelling benefits is their ability to support high bandwidth, accommodating the ever-growing demand for data by both consumers and businesses. According to a report by the International Telecommunication Union, fiber optic technology can provide speeds of up to 1 Gbps, easily surpassing the capabilities of copper, which typically maxes out around 100 Mbps in standard applications. This immense capacity makes fiber optics ideal for supporting applications like streaming high-definition video, online gaming, and massive data transfer.
In addition to speed, fiber optic cables are also known for their reliability and durability. They are less susceptible to electrical interference, which means they can maintain signal integrity over longer distances without degradation. A study from the Fiber Optic Association highlighted that fiber optic installations can provide up to 40% lower maintenance costs over their lifespan compared to copper counterparts due to their strength and resistance to environmental factors. Thus, as more organizations migrate towards digital infrastructure, the adoption of fiber optic technology is becoming not just beneficial, but essential for ensuring robust and efficient telecommunications systems.
Top 5 Core Cable Types That You Need To Know For Your Projects - Exploring Fiber Optic Cables: Advantages for Modern Telecommunication
| Cable Type | Core Material | Transmission Speed (Gbps) | Distance (m) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Mode Fiber | Glass | 100 | 10,000+ | Telecommunications, Internet |
| Multi-Mode Fiber | Glass | 40 | 300 | Data Centers, LANs |
| Armored Fiber | Glass | 100 | 10,000+ | Rugged Environments |
| Tight-Buffered Fiber | Glass | 10 | 100 | Internal Wiring |
| Loose-Tube Fiber | Glass | 100 | 10,000+ | Outdoor Installations |
Comparing Aluminum Core Cables: Cost and Efficiency in Electrical Projects
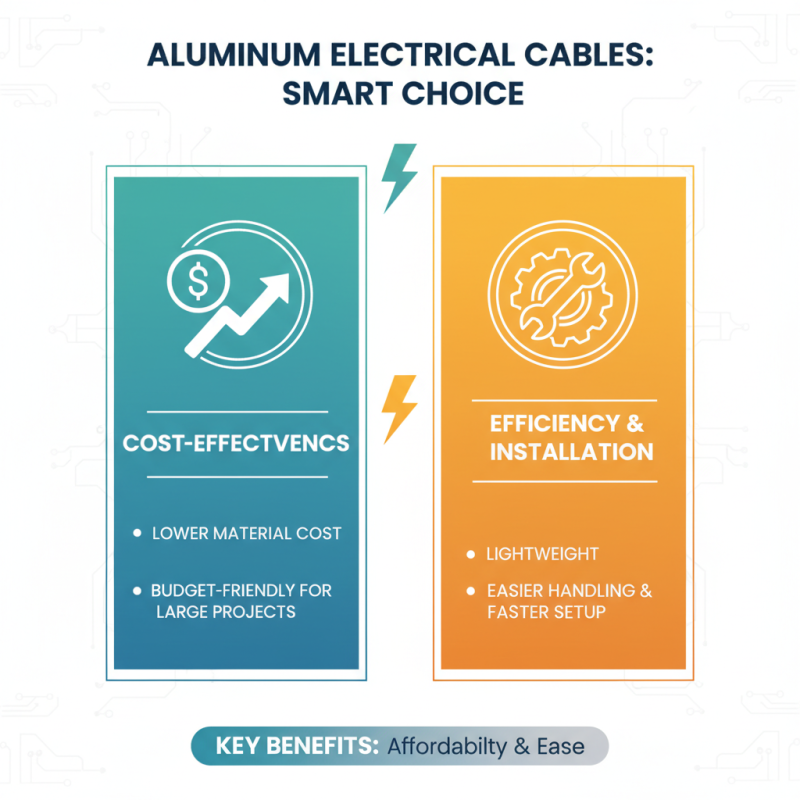
When it comes to electrical projects, selecting the right cable type is crucial for ensuring cost-effectiveness and efficiency. One of the most common materials used for electrical cables is aluminum. Aluminum core cables are often favored for their lower cost compared to copper, making them an attractive option for budget-conscious projects. Their lightweight nature also allows for easier handling and installation, particularly in larger projects where weight can be a significant factor.
However, while aluminum cables are economical, it is essential to consider their efficiency in terms of conductivity and long-term performance. Aluminum has lower conductivity than copper, which can lead to a voltage drop over distance, potentially affecting the overall efficiency of electrical systems. Additionally, it requires proper connections and may necessitate the use of specialized fittings to prevent overheating issues. Hence, when comparing aluminum core cables for your projects, it’s vital to weigh the initial cost savings against potential operational inefficiencies and maintenance requirements. Proper planning and understanding of these factors can lead to informed choices that achieve both budgetary and functional goals in electrical installations.
Related Posts
-

Top Electrical Connectors for Reliable Performance in Your Projects
-

2025 Top 10 Marine Cable Innovations Transforming Global Connectivity
-

Essential Automotive Cable Maintenance Tips for a Smooth Ride
-

10 Best Multi Conductor Cables for Superior Electrical Performance in 2023
-

Understanding Multi Conductor Cables: Essential Tips for Effective Electrical Wiring
-

Top Benefits of Using Lead Cable for Your Electrical Projects
