What You Need to Know About Power Wire Types?
When dealing with electrical systems, understanding power wire types is essential. Power wires come in various sizes, materials, and configurations. Each type serves a unique purpose. For example, copper wires are popular due to their excellent conductivity. They are widely used for residential wiring. Aluminum wires, on the other hand, are lighter and more cost-effective. They are often seen in industrial settings.
Choosing the right power wire is not just about cost. It’s also about safety and efficiency. Poor choices can lead to overheating or even fires. You need to consider the wire's gauge, insulation type, and voltage capacity. Higher gauge numbers indicate thinner wires, which carry less current. This choice can affect the overall performance of your electrical setup.
In electrical installations, mistakes can lead to significant issues. Poorly rated wires may fail under load. Understanding the implications of your choices is crucial. Each power wire type has its pros and cons. It's important to reflect on these details. The right selection not only ensures functionality but also helps in preventing hazards.
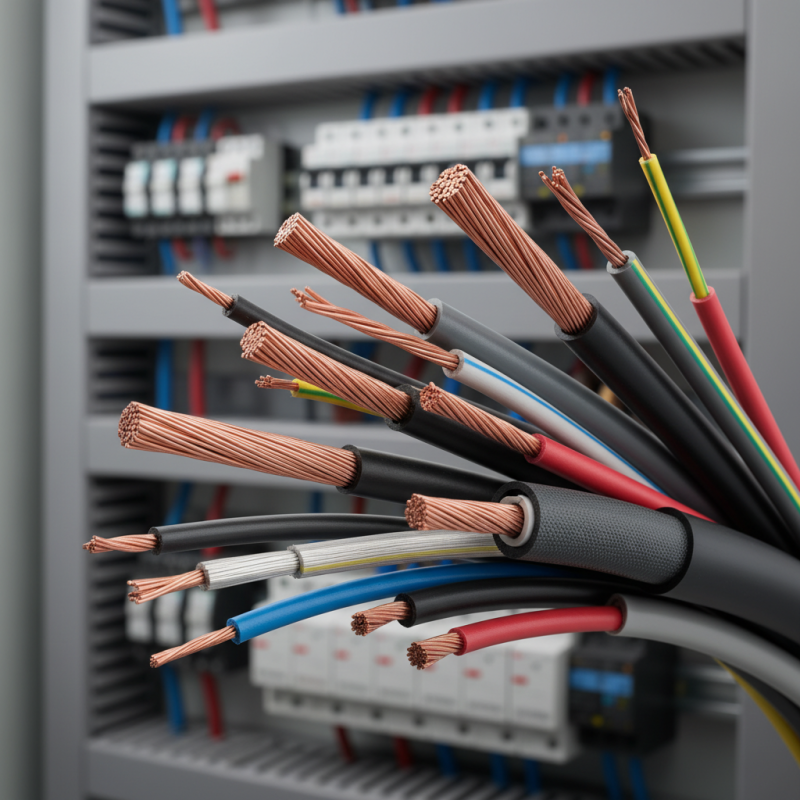

Understanding Power Wire Types: An Overview
When it comes to power wires, understanding their types is essential. Each type serves a specific purpose. For example, there are insulated, uninsulated, and multi-stranded wires.
Insulated wires protect users from electric shocks. They come in various colors, making identification easier. However, not all insulated wires are suitable for every environment.
Uninsulated wires are often used in specific applications, such as grounding. They are usually bare and need careful handling.
Multi-stranded wires, on the other hand, offer flexibility. They are commonly used in applications requiring frequent movement. Yet, their construction can make them more vulnerable to wear and tear.
It’s crucial to choose the right wire type based on your needs. Consider factors such as voltage, current, and environmental conditions. Mistakes in wire selection can lead to dangerous situations. Unmatched wire specifications may cause overheating or electrical failures. Understanding the nuances of power wire types will enhance safety and efficiency.
Key Characteristics of Different Power Wire Types
When considering power wire types, it’s crucial to understand their key characteristics. Different wire types are designed for specific applications.
For instance, copper wires are known for excellent conductivity. They are flexible and often used in residential settings. Aluminum wires are lighter and more cost-effective, but they may require special connectors.
Tips: Always check the wire gauge before installation. A thicker gauge can handle more current.
Another important aspect is insulation. Thermoplastic insulation is common. It’s effective but can deteriorate under high heat. Rubber insulation offers better heat resistance but can be harder to work with. Balancing cost and performance is often tricky.
Tips: Don’t overlook wire length. Longer wires can lead to energy loss. Assess your needs carefully before making a choice.
Common Applications for Various Power Wire Types

When considering power wire types, their applications vary significantly. Copper and aluminum wires are the most common. Copper wire handles high current loads effectively and is often used in residential wiring. Its excellent conductivity ensures efficient power transmission. On the other hand, aluminum wire is lighter and cheaper. It is frequently found in larger installations, like commercial buildings.
Data from the National Electrical Manufacturers Association indicates that over 65% of electrical installations use copper wiring. However, aluminum wires account for about 25% of installations due to cost considerations. This highlights a notable trade-off between performance and budget. Yet, safety concerns persist. Improper connections with aluminum can lead to overheating.
For industrial applications, specialized wires are crucial. High-temperature wires are needed in manufacturing. They can withstand extreme conditions. Despite advancements, issues remain. Resistance to wear can be a concern in rugged environments. Regular inspections are necessary to maintain safety and performance standards. Ignoring these can lead to serious hazards.
Safety Considerations When Using Power Wires
When dealing with power wires, safety is paramount. A significant number of electrical accidents stem from improper use of wires. According to the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), over 50,000 home fires are linked to electrical malfunctions each year. Choosing the right wire type is critical, but understanding how to use them safely is even more vital.
One key safety consideration is wire insulation. Wires must have appropriate insulation for their environment. For instance, wires in wet conditions should have waterproof ratings. An estimated 30% of electrical accidents could be avoided with proper insulation and maintenance. Additionally, wires should be sized correctly for the load they carry. Undersized wires can lead to overheating and result in fires. A study from the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) found that 20% of electrical fires were due to this oversight.
It's also crucial to check for fraying or damage regularly. Damaged wires can expose conductors, increasing the risk of electric shock. A shocking statistic from the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission revealed that about 2,000 people receive electric shocks annually due to faulty wiring. Therefore, maintaining a habit of inspection can drastically improve safety outcomes. Awareness and responsibility in handling power wires can prevent hazards effectively.
Choosing the Right Power Wire for Your Needs
Choosing the right power wire is critical for safety and efficiency. Different applications require unique wire types. For example, low-voltage applications typically use thinner wires, while high-power appliances need thicker gauge wires to handle the current safely.
According to a report from the National Electrical Code, using the wrong wire gauge can cause overheating. Overheating can lead to equipment failure or even fire hazards. In residential wiring, 60% of fire incidents are attributed to electrical failures. This statistic highlights the importance of selecting appropriate wire sizes.
Consider the environment where the wire will be installed. Wet or humid conditions require specific types of insulation to prevent short circuits. Additionally, wires may need to meet specific regulations based on their installation location. Many users overlook these factors, which can lead to costly mistakes. Remember, not all power wires are created equal. Being informed can make a significant difference in performance and safety.
What You Need to Know About Power Wire Types? - Choosing the Right Power Wire for Your Needs
| Wire Type | Current Rating (A) | Voltage Rating (V) | Applications | Insulation Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWG 14 Copper | 15 | 600 | Lighting, Small Appliances | PVC |
| AWG 12 Copper | 20 | 600 | Circuit Wiring, Power Tools | PVC |
| AWG 10 Copper | 30 | 600 | Heavy Equipment, Larger Appliances | PVC |
| AWG 8 Copper | 50 | 600 | Subpanel Feeders, Industrial Equipment | XLPE |
| AWG 6 Copper | 65 | 600 | Generators, Welders | XLPE |
Related Posts
-

Why is Power Wire Essential for Electrical Safety and Efficiency?
-
How to Choose the Right Power Wire for Your Electrical Projects?
-
Why Are Electrical Connectors Essential for Reliable Electrical Connections?
-
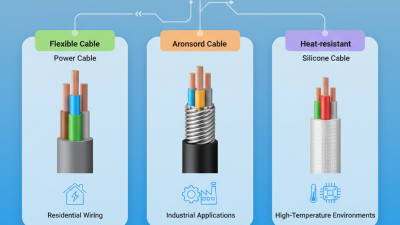
Top 3 Core Cable Types You Need to Know for Your Electrical Projects
-

2025 Top 5 Industrial Electric Wire and Cable Solutions for Every Business Need
-
2026 Top Multi Conductor Cable Types and Their Applications?
