Understanding Lead Cables: Essential Insights for Safe Electrical Installations
Lead cables are a critical component in the realm of electrical installations, serving as conduits for power transmission in various applications. According to a report from the International Electrotechnical Commission, the inappropriate use or maintenance of lead cable can lead to safety hazards, contributing to nearly 15% of electrical failures in industrial settings. In addition, the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers highlights that improper handling of lead cables can result in significant downtime and costly repairs, impacting both productivity and safety.
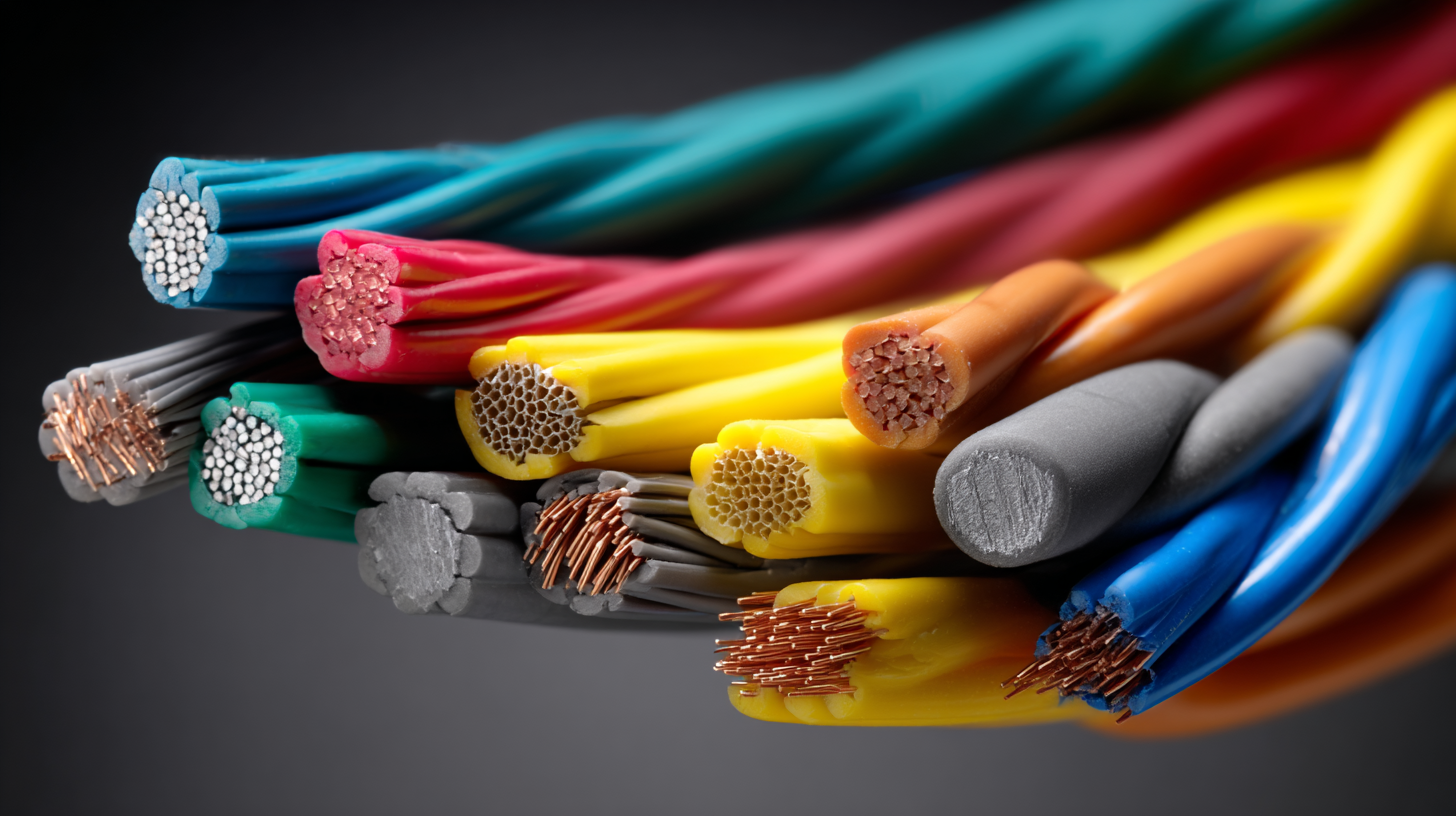
Understanding the key characteristics, installation processes, and safety measures related to lead cables is essential for professionals to ensure compliance with regulatory standards and enhance the reliability of electrical systems. This guide aims to provide in-depth insights into lead cables, emphasizing best practices for their installation and maintenance to promote both safety and efficiency in electrical projects.
Key Components of Lead Cables for Electrical Installations
Lead cables are crucial in electrical installations, specifically designed to ensure safety and efficiency. One of the key components of lead cables is the insulation material. According to the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), effective insulation is essential for preventing electrical shocks and short circuits, ensuring the longevity of electrical systems. Common materials used for insulation include thermoplastic elastomers, which provide excellent flexibility and resistance against environmental factors such as heat and moisture.
Another significant component is the conductor, typically made of copper or aluminum. The choice of conductor material significantly impacts the cable's performance. As per a report by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), copper conductors are preferred for their superior conductivity and lower resistance, resulting in less energy loss. The size of the conductor is also critical; it must be appropriately rated for the expected current load to prevent overheating and potential failures. A well-designed lead cable, featuring quality insulation and optimal conductor sizing, plays a vital role in maintaining safety and efficiency in electrical installations.
Understanding Lead Cables: Essential Insights for Safe Electrical Installations
Safety Precautions When Working with Lead Cables
When working with lead cables, safety precautions are paramount to ensure both personal and environmental safety. Lead is a toxic material, and exposure can occur through inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact. Proper personal protective equipment (PPE) should always be worn, including gloves, masks, and protective clothing. Additionally, it is crucial to work in a well-ventilated area to minimize the risk of lead dust accumulation, which can pose serious health risks to workers.
Before beginning any installation or maintenance work, it is essential to conduct a thorough risk assessment of the area. Ensure that lead cables are properly labeled and identify any potential hazards in the surroundings. Using specialized tools designed for handling lead cables can further reduce the risks of accidental exposure. Finally, proper disposal methods for any lead-containing waste must be followed in accordance with regulatory guidelines to prevent environmental contamination. By adhering to these safety precautions, workers can help mitigate the dangers associated with lead cables and ensure safer electrical installations.
Guidelines for Selecting the Right Lead Cable for Your Project
When selecting the right lead cable for your electrical project, understanding the specifications and standards is crucial. According to the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), using the appropriate cable type and size can improve system efficiency and reduce energy costs by up to 20%. Consider factors such as cable length, insulation type, and voltage requirements. For instance, PVC insulation is generally rated for lower voltages, making it suitable for residential applications, while cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) insulation offers higher temperature resistance and is often used in industrial settings.

Moreover, the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) provides guidelines on cable ratings and environmental considerations. For example, choosing a lead cable that meets the IEC 60502 standard ensures compliance with safety and performance requirements, minimizing risks of electrical failures. According to a recent industry report, projects utilizing certified cables reported a decrease in maintenance costs by approximately 15% over their operational lifetime. Therefore, ensuring that your lead cables align with these standards is not only a matter of safety but also a crucial component for long-term project success.
Best Practices for Installing Lead Cables to Ensure Safety
When it comes to installing lead cables, ensuring safety is paramount. Lead cables are widely used in various electrical applications due to their flexibility and robustness. However, improper installation can pose significant risks, including electrical hazards and degradation of performance over time. To mitigate these risks, it is essential to adhere to best practices during installation. This includes thorough inspection of the cable and components before installation, ensuring that the environment is suitable and that appropriate protective gear is used.
Furthermore, maintaining proper cable management is crucial. This involves securing cables in place with the correct fittings, avoiding excessive bending, and ensuring adequate protection from external elements. Regular maintenance and monitoring should also be part of the installation process to ascertain that the cables remain in good condition. By following these guidelines, not only is the integrity of the installation maintained, but the safety of individuals and the surrounding environment is also ensured. As the demand for reliable cable solutions continues to grow, implementing stringent safety measures will further enhance operational effectiveness in electrical installations.

Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Lead Cables in Installations
When working with lead cables in electrical installations, it is crucial to avoid some common pitfalls that could compromise safety and functionality. One significant mistake is failing to properly assess the insulation condition of the lead cables. Over time, insulation can degrade due to environmental factors or physical wear, leading to potential hazards like short circuits or electrical shocks. Regular inspections and maintenance are essential to ensure that the cables remain safe for use.
Another common error is neglecting to follow manufacturer specifications regarding load capacities and installation procedures. Exceeding the recommended electrical load can lead to overheating and, in extreme cases, equipment failure or fire. Additionally, improper cable connections can create resistance points, resulting in power loss or damage to devices connected to the system. Adhering strictly to guidelines and using the correct materials during installation will significantly enhance safety and efficiency, ensuring that electrical systems operate as intended.
Understanding Lead Cables: Essential Insights for Safe Electrical Installations
| Dimension | Description | Common Mistakes |
|---|---|---|
| Cable Type | Types of lead cables available for use. | Using the wrong type for specific applications. |
| Voltage Rating | The maximum voltage the lead cable can handle. | Exceeding the cable's voltage rating. |
| Installation Environment | Conditions in which the cable is installed (temperature, humidity). | Ignoring environmental factors affecting performance. |
| Connection Points | Where the cable connects to devices. | Poor connections leading to short circuits. |
| Maintenance | Periodic checks and upkeep of cables. | Neglecting regular maintenance checks. |
Related Posts
-

Understanding Multi Conductor Cables: Essential Tips for Effective Electrical Wiring
-

The Ultimate Guide to Understanding Different Wire Connector Types for Your Projects
-
Exploring the Advantages of 4 Core Cable in Modern Electrical Installations and Its Impact on Efficiency
-

Exploring the Essential Role of Power Wires in Modern Electrical Systems
-
Understanding the Benefits and Uses of Romex Wire in Modern Electrical Installations
