What is Wire and Cable and How Are They Used in Everyday Applications?
Wire and cable play crucial roles in modern society. They are essential for electricity distribution, telecommunications, and various industrial applications. According to a report by the International Wire and Cable Manufacturers Association, the global wire and cable market was valued at over $200 billion in 2021, showcasing its importance in everyday life.
In our daily routines, wires connect homes to power sources and enable communication. For instance, fiber optic cables provide high-speed internet, which has transformed how we interact. However, many overlook the complexities involved in manufacturing and maintaining these systems. The quality of cable materials can significantly affect both performance and safety.
Despite incredible technological advancement, we must reflect on issues such as waste in cable production and improper disposal. Approximately 50 million tons of electronic waste is generated globally each year, often containing discarded wires and cables. Addressing these concerns is vital for sustainability. We need a deeper understanding of wire and cable's life cycle to make responsible choices.

Definition and Types of Wire and Cable in Electrical Engineering
Wire and cable play crucial roles in electrical engineering. They are essential for transmitting electricity and data. Wires are typically made of conductive materials, while cables consist of multiple wires housed together. The most common types of wire include copper and aluminum, known for their excellent conductivity. Cables, on the other hand, can include power cables, data cables, and coaxial cables, each serving a specific purpose.
Power cables carry electricity from one point to another. They are thicker and insulated to handle high voltages. Data cables, such as Ethernet and USB, allow devices to communicate and transfer data. Coaxial cables, often used for television signals, are designed to minimize interference. Each type has unique characteristics and applications, but all require careful handling and installation.
Understanding wire and cable types helps in choosing the right one for a project. Mistakes in selection can lead to inefficiencies or failures. For instance, using a data cable instead of a power cable might cause malfunctions. Observing installation guidelines is also essential. Ignoring these can result in hazardous situations. Always consider the specific needs of the application to ensure safety and functionality.
What is Wire and Cable and How Are They Used in Everyday Applications?
| Type of Wire/Cable | Description | Common Applications | Material |
|---|---|---|---|
| Copper Wire | Highly conductive and flexible | Electrical wiring, electronics | Copper |
| Aluminum Wire | Lightweight and cost-effective | Power distribution, overhead lines | Aluminum |
| Fiber Optic Cable | Transmits data as light signals | Internet, telecommunications | Glass or plastic fibers |
| Coaxial Cable | Consists of inner conductor and outer shield | Television, broadband internet | Copper, plastic insulation |
| Twisted Pair Cable | Pairs of wires twisted together to reduce interference | Telephone, local area networks (LAN) | Copper |
Key Materials Used in Wire and Cable Manufacturing

When discussing wires and cables, it's essential to understand the materials used in their manufacturing. Copper is one of the most common materials for wires. It offers excellent conductivity. This makes it ideal for electrical wiring in homes and appliances. However, copper can be expensive. Some manufacturers opt for aluminum instead, which is lighter and more affordable but less conductive.
Another key material is insulation. PVC, or polyvinyl chloride, is widely used for insulating wires. It is durable and resistant to moisture. Yet, it may degrade under high temperatures, posing potential risks. Additionally, cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) is increasingly popular. It can withstand higher temperatures and provides better protection against electrical stress.
In some applications, specialized materials like rubber or silicone are preferred for their flexibility. These are often found in portable electronic devices. However, these materials might not be as robust as others in harsh environments. Each choice involves trade-offs, balancing performance, cost, and usability. Understanding these materials can lead to better decisions in everyday applications.
Applications of Wire and Cable in Residential Electrical Systems
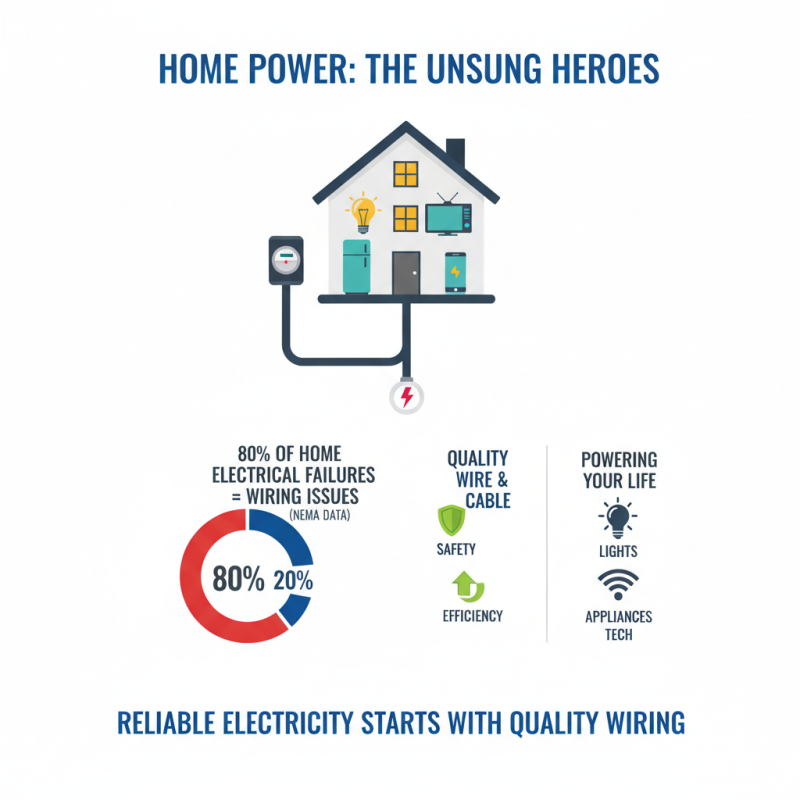
Wire and cable are essential components in residential electrical systems. They facilitate the distribution of electricity throughout homes, powering everything from lights to appliances. According to the National Electrical Manufacturers Association, over 80% of residential electrical failures can be traced back to issues with wiring. This highlights the crucial role that quality wire and cable play in safety and efficiency.
In many households, outdated wiring poses risks. For example, homes built before the 1980s may still use aluminum wires, which are less conductive than copper and can lead to overheating. A recent study indicated that nearly 25% of older homes have wiring that fails to meet modern standards. Upgrading wiring not only improves safety but also increases energy efficiency. Energy-efficient appliances require reliable wiring to function optimally, which is essential as we transition to greener technologies.
Electrical codes exist for a reason. They help ensure safe installation practices. Yet, many homeowners overlook the importance of following these guidelines. Simple mistakes can lead to costly repairs. It’s vital to consult professionals who can assess and update wiring. Proper installation and maintenance of wire and cable can prevent hazards and improve the reliability of residential electrical systems. Investing in quality materials and skilled labor saves money in the long run.
Industrial Uses of Wire and Cable in Manufacturing Processes
Wire and cable play a crucial role in various industrial applications. In manufacturing, they are essential for machinery, robotic systems, and conveyor belts. According to a recent market report, the global wire and cable market is projected to reach $250 billion by 2025. This growth highlights the increasing need for reliable electrical connections across industries.
In factories, wires provide power to equipment. Without them, production halts. Automated systems rely on intricate wiring for seamless operation. This highlights how essential wires are to efficiency. However, maintaining these systems can be challenging. Worn-out cables can lead to machinery failures and safety hazards.
**Tip:** Regularly inspect wiring and cables. Look for fraying or signs of wear. This proactive approach helps prevent unexpected downtimes. Also, ensure proper insulation to avoid electrical leakage. Proper care can extend the lifespan of these crucial components.
Industrial Uses of Wire and Cable in Manufacturing Processes
Emerging Technologies and Trends in Wire and Cable Industry
The wire and cable industry is undergoing remarkable changes. Emerging technologies, such as advanced materials and smart cables, are transforming their applications. These innovations enhance electrical performance and improve durability. For instance, flexible conductors now efficiently transmit data and energy in confined spaces.
Industry trends also reveal a focus on sustainability. Manufacturers are exploring eco-friendly materials. Biodegradable cables are gaining attention. These cables minimize environmental impact while maintaining high performance. However, the adoption of new technologies can be slow. Many companies hesitate to invest in unproven solutions.
Another noticeable trend is the development of connectivity solutions. With the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), cables must support increased data transfer. High-speed connectivity is essential. Yet, integrating these solutions poses challenges. Transitioning from traditional methods requires careful planning and adjustment. The industry is gradually adapting, but challenges remain.
Related Posts
-
Understanding the Essential Role of Wire and Cable in Modern Technology Systems
-

2025 Top 5 Industrial Electric Wire and Cable Solutions for Every Business Need
-
Top 10 Control Cable Types for Optimal Performance in Industrial Applications
-
Why Choose a 4 Wire Cable for Your Electrical Projects?
-
What is Lead Wire and Its Applications in Various Industries?
-

Top 10 Uses of Thermocouple Wire in Industrial Applications
